Homomorphic Encryption
Definition of HE
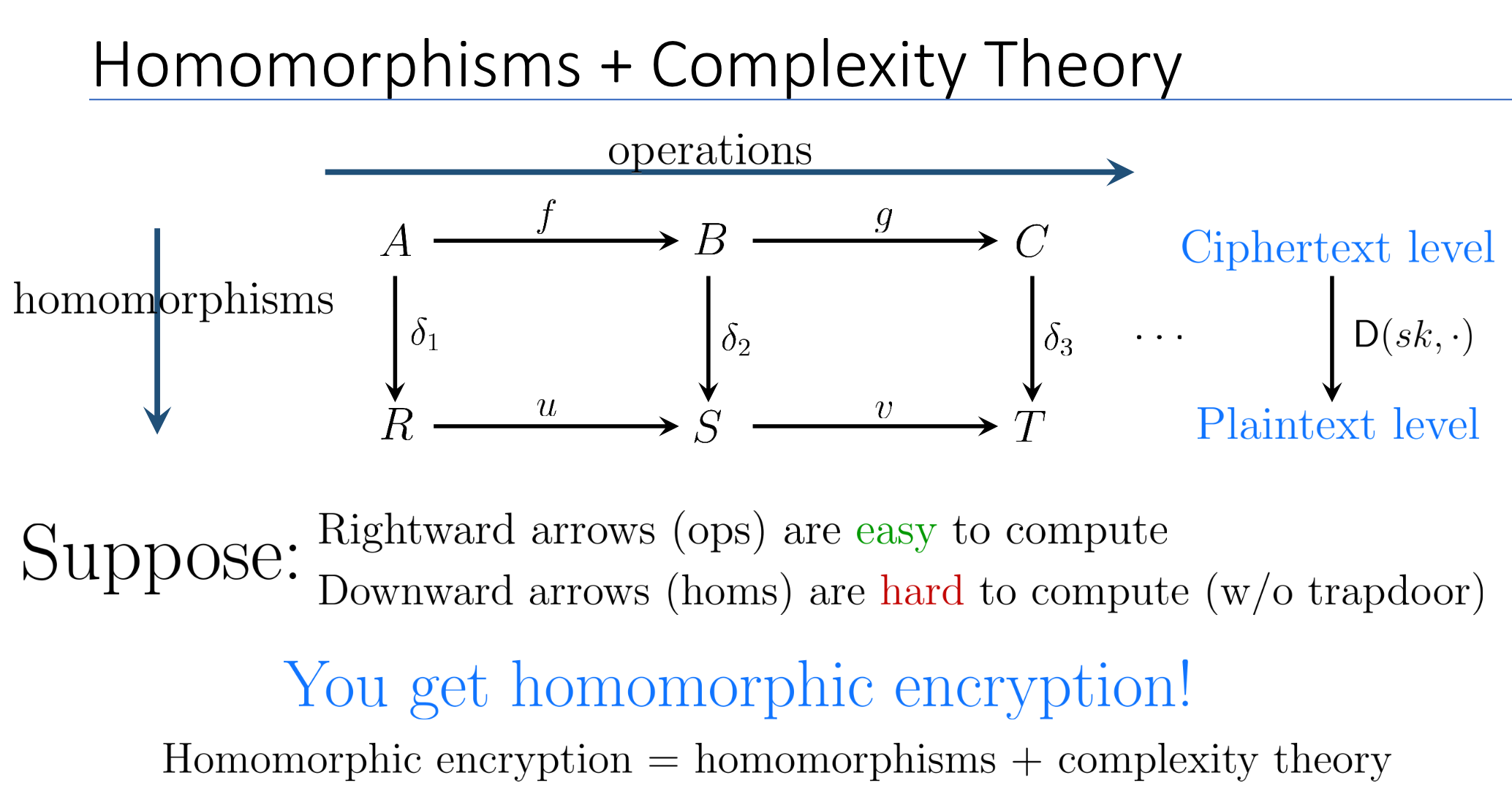
- Procedures:
and (for "Evaluate") - Correctness: For any function
(a family of functions), and any ciphertexts ,
Set, then . - Security: Same as basic PKE. Again, many
's per .
How
- Family of functions: A homomorphic encryption scheme only works for
(a family of functions). - Arithmetic Circuit: A layered graph of
and gates. 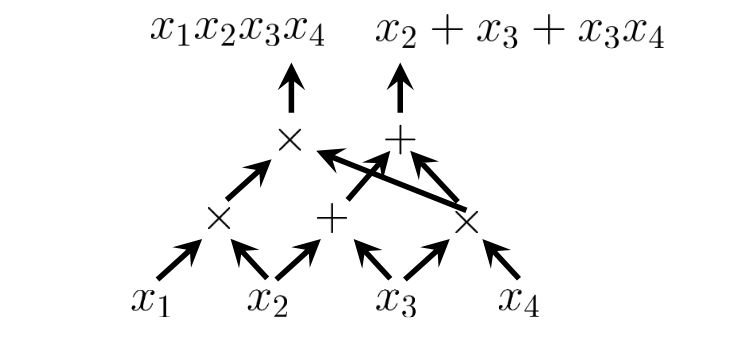
- Fully Homomorphic Encryption(FHE): Family of functions
all efficiently computable functions — e.g., all arithmetic circuits.
History
1978: Rivest, Adleman, Dertouzos "On Data Banks and Privacy Homomorphisms"
- They throw a question: Can we delegate the processing of data without giving away access to it?
2009: Gentry "Fully Homomorphic Encryption Using Ideal Lattices"
- What if a homomorphic encryption scheme could decrypt itself with an encrypted secret key? (bootstrap)
https://crypto.stackexchange.com/questions/42666/what-exactly-is-bootstrapping-in-fhe
https://dualitytech.com/blog/bootstrapping-in-fully-homomorphic-encryption-fhe/
Quantum kills all HE schemes using abelian groups!
Thm. [Watrous] Let
The attack [Armknecht et al. '14]:
- Encryption of
(group identity) are a subgroup of - Compute generators
of by encrypting 's - Challenge ciphertext
iff
Why Noise Accumulates in FHE
- Encryption Process:
- When a plaintext message is encrypted using FHE, a certain amount of noise is deliberately added to the ciphertext. This noise is essential for ensuring the security of the encryption scheme. The initial noise level is typically small enough that the ciphertext can be decrypted correctly.
- Homomorphic Operations:
- Homomorphic operations (addition and multiplication) on ciphertexts are performed in such a way that the operations correspond to the same operations on the underlying plaintexts. However, these operations also increase the noise level in the resulting ciphertext.
- Each homomorphic addition increases the noise linearly.
- Each homomorphic multiplication increases the noise quadratically. This is because the noise in the product ciphertext is roughly the product of the noise levels of the two operand ciphertexts.
- Repeated Operations:
- As more homomorphic operations are performed, the noise continues to accumulate. After many operations, the noise level can become so high that it interferes with the decryption process, making it impossible to recover the original plaintext correctly.
Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping in Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) is a technique used to refresh the ciphertext to prevent it from becoming too noisy during computation.
- In FHE, ciphertexts accumulate noise as they undergo homomorphic operations. If the noise level becomes too high, the ciphertext can no longer be decrypted correctly.
Bootstrapping helps to reset this noise, allowing more computations to be performed on the encrypted data without decrypting it.
- Noise Accumulation:
- Each homomorphic operation (addition or multiplication) adds a certain amount of noise to the ciphertext. As more operations are performed, the noise increases.
- If the noise exceeds a certain threshold, the ciphertext becomes undecipherable, meaning the decryption will fail to produce the correct result.
- Bootstrapping:
- Bootstrapping is a process where a noisy ciphertext is decrypted and then re-encrypted, but this is done homomorphically.
- The key idea is to use a homomorphic encryption scheme that can evaluate its decryption function. By doing this, the ciphertext is “refreshed,” meaning the noise level is reduced, and further computations can be performed on it.
- Decryption Circuit: The FHE scheme can evaluate the decryption circuit on a ciphertext using another ciphertext that encrypts the secret key. This process produces a new ciphertext with reduced noise.
- Implementation Steps:
- Evaluate Decryption Homomorphically: Given a ciphertext c and an encrypted secret key sk_enc, the FHE scheme evaluates the decryption function homomorphically:
- D(c, sk_enc), resulting in a new ciphertext c' that encrypts the same plaintext but with less noise.
- Re-encryption: The result of the homomorphic decryption is re-encrypted to produce a fresh ciphertext.
- Evaluate Decryption Homomorphically: Given a ciphertext c and an encrypted secret key sk_enc, the FHE scheme evaluates the decryption function homomorphically:
- Benefits of Bootstrapping:
- Unlimited Computations: By periodically applying bootstrapping, it is possible to perform an unlimited number of homomorphic operations without worrying about the noise level becoming too high.
- Maintain Ciphertext Integrity: Bootstrapping ensures that the ciphertext remains valid and decryptable throughout extensive computations.